NEWS/RELEASE
Announcement of Joint Research with Kyoto University – Identifying the ‘Active Sites’ of Oxygen Generation Reaction, Taking a New Step Towards the Realization of a Green Hydrogen Society
Multimodal analysis reveals the active site key to the oxygen evolution reaction (OER): Uncovering how the structure of an iridium oxide catalyst drives its exceptional performance
August 20, 2025
A research group led by post-doctoral researcher Dr. Neha Thakur and Professor Yoshiharu Uchimoto of the Graduate School of Human and Environmental Studies, Kyoto University, in collaboration with TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd., the FC-Cubic Technology Research Association, Yokohama National University, Kyushu University, Nara Women’s University, Shimane University, and Ritsumeikan University, has elucidated the origin of the high activity of iridium oxide catalysts in the oxygen evolution reaction (OER), which is a key process in water electrolysis for hydrogen production.
The production of green hydrogen via water electrolysis powered by renewable energy plays an essential role in energy systems aimed at achieving carbon neutrality. Polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) water electrolysis is a highly efficient method for producing high-purity hydrogen, and the characteristics of the catalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) are critical to further improving efficiency. Although iridium-containing oxides are used as OER catalysts, the reactions occurring on electrode surfaces with hierarchical structures are governed by complex factors. Until now, it has been unclear which factors determine catalyst performance, making it difficult to establish development guidelines.
This achievement supports the development of highly efficient and stable PEM water electrolysis. In catalyst development, where the factors determining catalytic activity had previously been unknown, this research demonstrates the importance of multimodal analysis, which integrates multiple advanced analytical techniques. By applying this method, it is now possible to develop catalysts with dramatically improved performance, offering the potential to become one of the fundamental technologies for realizing a decarbonized society.
The results of this research will be published online in the Journal of the American Chemical Society of the American Chemical Society on August 19, 2025.
<Paper Title and Authors>
Title: Identifying Active Sites of IrOx Catalysts for OER: A Combined Operando XAS, SEIRAS, and Theoretical Study
Authors: Neha Thakur, Yadan Ren, Mukesh Kumar, Tomoki Uchiyama, Mitsuharu Fujita, Ikkei Arima, Minoru Ishida, Yingkai Wu, Yuta Tsuji, Hideto Imai, Masashi Matsumoto, Yu Zhuang, Kentaro Yamamoto, Toshiyuki Matsunaga, Koji Ohara, Mitsuhiro Matsumoto, Yuki Orikasa, Yoshiyuki Kuroda, Shigenori Mitsushima, Yoshiharu Uchimoto
Publication: Journal of American Chemical Society DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c18510
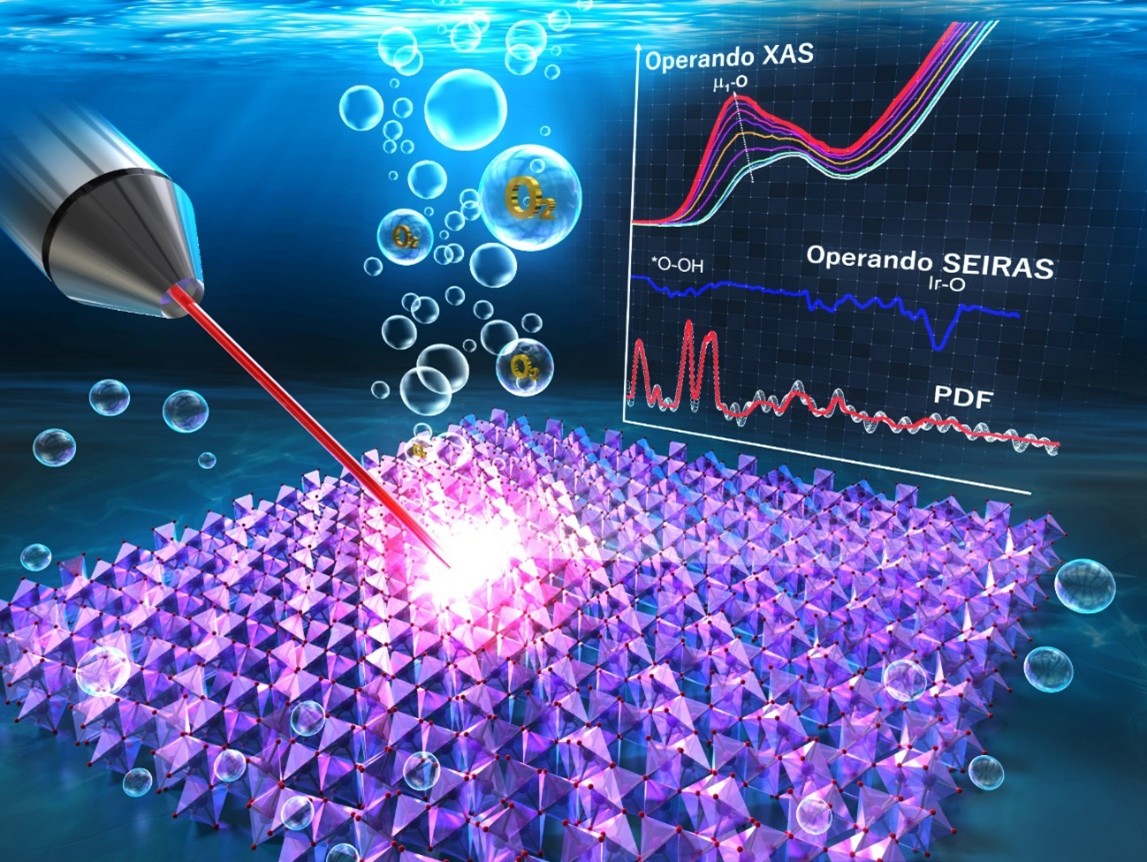
This diagram shows how the structure of the iridium oxide surface is analyzed
multimodally using X-rays while a potential is applied, i.e., while water electrolysis is occurring.
TANAKA offers highly active and durable Ir oxide anode catalysts and Pt-based cathode catalysts as electrocatalysts for PEM-type water electrolysis. We are also developing catalysts to prevent H2 leaks and Ir reduction catalysts. We are pleased to inform that recently we received the 2025 Technology Award from the Catalyst Manufacturers Association, Japan (CMAJ) for development and practical application of electrode catalysts for PEM water electrolysis.
This technology involves the development and commercialization of a new catalyst with dual functions: oxygen evolution reaction (OER) and gas recombination catalyst (GRC). This catalyst technology efficiently reduces the hydrogen concentration on the anode side while maintaining high electrolysis efficiency during the water electrolysis reaction, successfully resolving the “hydrogen crossover” phenomenon, a technical issue in PEM water electrolysis. Furthermore, this catalyst enables thinner membrane thickness, significantly improving safety and electrolysis efficiency.
For more information, please visit the product page on our industry website:
Electrocatalysts for Fuel Cell / Water Electrolysis (PEM type)|TANAKA
Information about the “2025 Catalyst Industry Association Technology Award”:
TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL TECHNOLOGIES Receives 2025 Technology Award from Catalyst Manufacturers Association, Japan, for Development and Practical Application of Electrode Catalysts for PEM Water Electrolysis | TANAKA
Information related to the published article: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.4c18510
