One common solution to improve the safety of LIBs is using thermal-conducting interlayers, materials designed to even out the temperature between a battery’s modules, bringing it to between 15 to 45 °C. To ensure that a high-capacity LIB is safe, these materials should be highly thermally insulating, thus preventing the propagation of heat, while also ensuring that temperature is uniformly distributed in the battery.
Researchers at Tsinghua University and Zhejiang University recently designed a new thermal-switching material that meets both criteria and can effectively regulate the temperature in high-capacity batteries. This material, introduced in Nature Energy paper, rapidly responds to temperature, enabling the safe cycling of batteries in varying operating conditions.
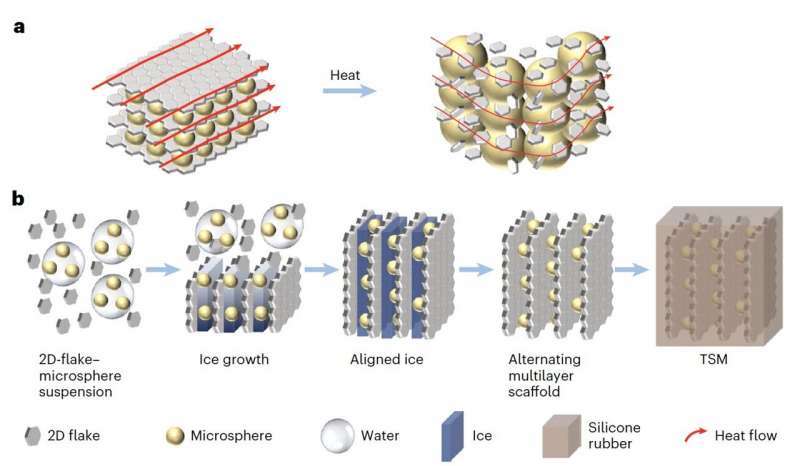
a, Thermal-switching mechanism of the TSM. Under normal working conditions, the thermally conductive network is complete for phonon transportation to ensure thermal conductivity above 1 W m−1 K−1. Under TR conditions, the 2D flakes are separated due to the thermally triggered volume expansion of the microspheres, resulting in a thermal conductivity lower than 0.1 W m−1 K−1. The width of the red arrows represents the strength of heat flux. b, The self-assembly process through freeze-casting of 2D-flake–microsphere suspensions to form an alternating multilayer scaffold together with polymer infiltration. Flakes and microspheres can be uniformly dispersed in water to form a slurry through high-speed stirring. During the freezing process, as microspheres are rich in hydroxyl groups, a graphene–water–microsphere core–shell structure tends to form during mixing processes, leading to the architecture where graphene sheets overlap with each other but closely connect with the thermally responsive microsphere layer. After freeze-drying, the alternating multilayer skeleton is obtained, followed by infiltration of silicone rubber to obtain the TSM.Credit: Nature Energy (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41560-024-01535-5.
“Effective thermal safety management relies on the thermal conductivity of interlayer materials, yet current designs lack the needed responsiveness for both performance and safety,” Wang, Feng and their colleagues wrote in their paper. “We design a thermal-switching material with high switching ratio from thermal conduction to thermal insulation state to address this predicament.”
The thermal-switching material designed by Wang, Feng and their colleagues is comprised of microspheres embedded between connected graphene layers. Notably, the microspheres expand in volume in response to changes in temperature.
The microspheres’ temperature-sensitive expansion disrupts the transport of heat by separating neighboring 2D graphene layers. In turn, this helps to regulate the temperature inside battery cells, preventing them from exploding.
To evaluate the performance of the material they designed, the researchers integrated it into a 50 Ah Ni–Co–Mn LIB, using it as a cell-to-cell interlayer. Their findings were highly promising, as the material was found to successfully act as a thermal regulator, preventing the propagation of heat and chain reactions that could lead to explosions.
TR propagation test for 50 Ah cell. Credit: Nature Energy (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41560-024-01535-5
“The designed thermal-switching material exhibits a wide temperature range for heat conduction (1.33 W m−1 K−1 at room temperature) and can transform to an adiabatic state within 30 s (0.1 W m−1 K−1 at around 100 °C) when heated,” Wang, Feng and their colleagues wrote.
“When applied as cell-to-cell interlayers for a module with four 50 Ah nickel–cobalt–manganese lithium-ion cells, the material not only ensures a uniform temperature distribution under normal working conditions, but more importantly prevents 80% of the heat transmission from thermal runaway, effectively avoiding catastrophic battery explosion.”
The new thermal regulator introduced by this research team could soon be implemented and tested on other high-capacity batteries. In the future, it could contribute to the widespread commercialization and use of these batteries, ensuring their safety in varying climates on Earth and at different operating conditions.
“We believe that this thermally responsive material design will ensure safety and high performance throughout the lifespan of high-energy-density battery modules,” said the researchers.
This article was written by Ingrid Fadelli from Tech Xplore and was legally licensed through the DiveMarketplace by Industry Dive. Please direct all licensing questions to legal@industrydive.com.