TANAKA's Initiatives for Power Devices

"Reliability" and "Innovation"
TANAKA has been involved in industrial precious metal materials for over 100 years and continues to provide innovative solutions for the semiconductor, electronic device, automotive, and energy industries. We offer total solutions unique to TANAKA.
Growing Power Device Market and Expectations for New Material Development
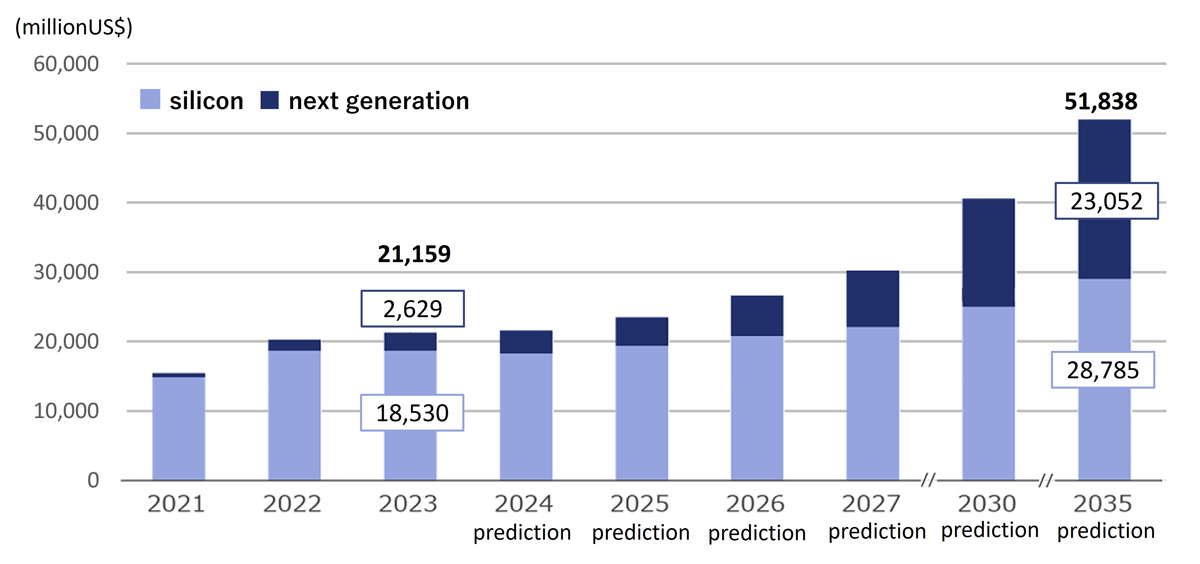
Source: Fuji Keizai, "Current Status and Future Outlook of the Next-Generation Power Device and Power Electronics Market 2024"
Power devices, which withstand high voltages and control high currents, are indispensable for vehicles, especially electric vehicles (EVs), and are a necessary technology in the infrastructure sector, including industrial machinery, railways, and heavy electrical equipment. They are also attracting attention from the perspective of energy saving, as they efficiently manage energy and help reduce energy consumption. Power devices are key devices essential for achieving energy savings and are used in a wide range of fields, including digital devices such as personal computers and smartphones, home appliances such as televisions and air conditioners, and even artificial satellites and next-generation communication base stations, with demand for them increasing. Along with the growing market needs, the development of new technologies is accelerating, and power devices are required to have higher output and efficiency. For each component, the development of new materials is needed that can respond to further miniaturization in addition to high heat dissipation, high heat resistance, and bonding reliability.
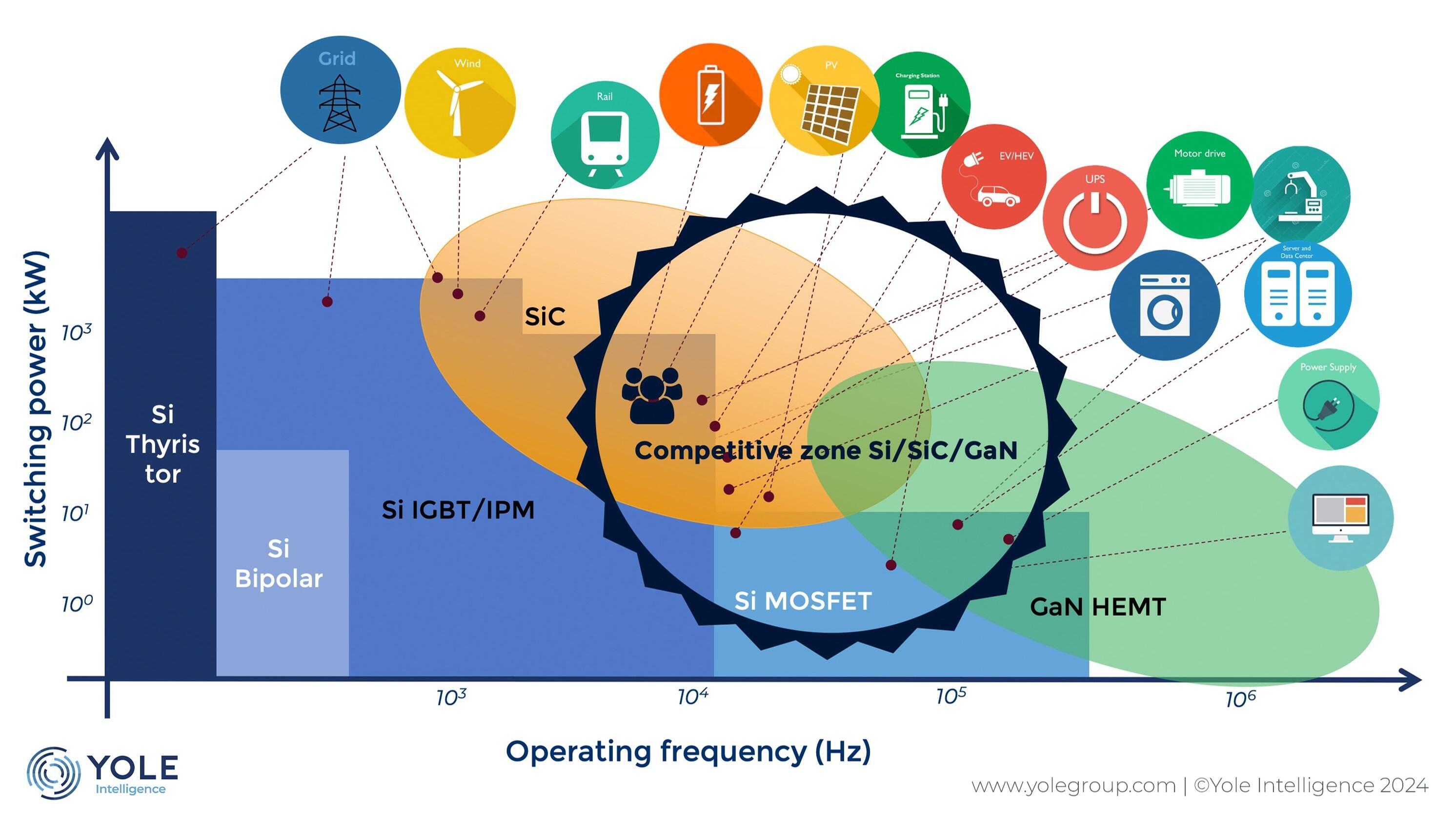
Source: Status of the Power Electronics Industry report, Yole Intelligence, 2023
Power devices are currently in a transitional period in which, in addition to technological improvements based on Si, which has been the mainstay so far, mass production and development of next-generation devices represented by SiC and GaN are being carried out. As miniaturization progresses, the need for materials with “low resistance” and “heat dissipation measures” will continue to grow in order to harness power performance.

Contributing to power devices with materials that
TANAKA's Products for Power Devices Offering Total Solutions
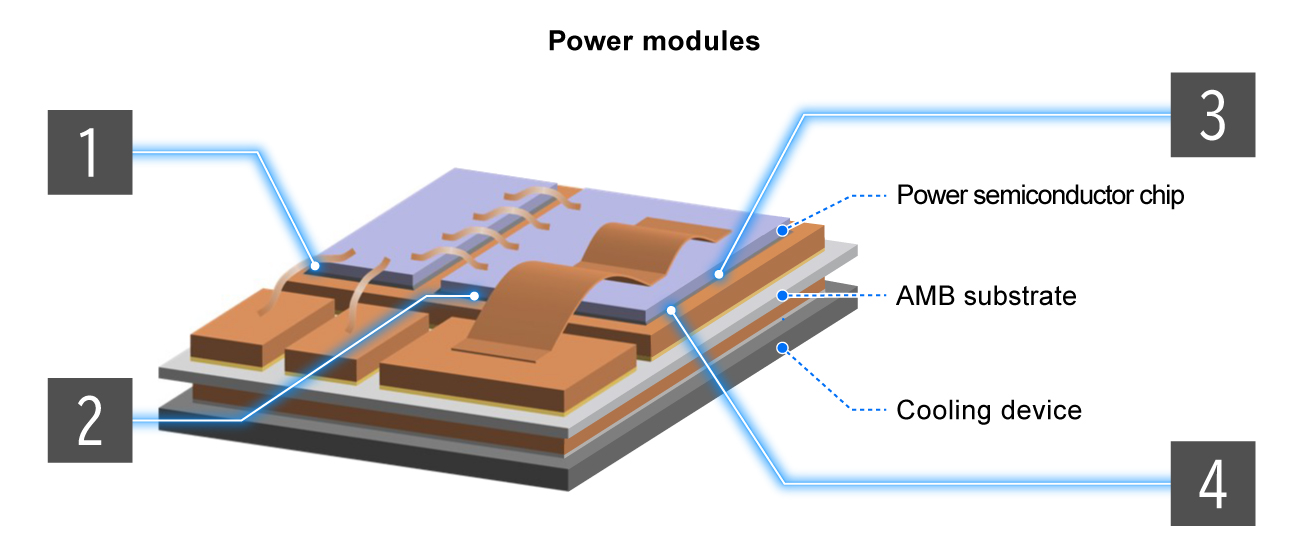


Bonding Wires
Al Wire/Ribbon
- High bondability
- High humidity resistance
Cu Wire/Ribbon
- Excellent electrical conductivity
- Excellent cutting current

Die Bonding Material
Ag Adhesive
- Good adhesion to bare Si
Hybrid Ag Adhesive
- High thermal conductivity
- High reliability
Sintered Pure Silver
- High thermal conductivity
- High thermal bonding strength


Active Brazing Filler Metal/Copper Composite Material
Thick Cu Circuit Formation
- Etching-free method
- Can be used for thin foil of solder material
Binderless
- Easy maintenance of the furnace
Reduced heat treatment time
- Low melting solder
 【Various Electrodes and Metallized Layers】
【Various Electrodes and Metallized Layers】Plating Processes
Metallized layer for bonding pads
- Ni/Pd/Au, Ni/Au, Ag, etc.
- Appropriate suggestions for the combination of bonding wire and pad materials
- Achieving high reliability and high production efficiency
Rear-side electrodes for ohmic contacts
- Ni/Au and others
- Suppresses wafer warpage under low stress
- Good bondability for die attachment
Lead frames, copper clips, and for PCBs
- Ni/Pd/Au, etc.
- Prevention of Ni layer diffusion
- Thinning Au layer to reduce overall costs

Sputtering Target
Various precious metal targets and alloy targets
- Pure precious metal targets such as Au, Ag, Pt, Pd, and Ir
- Precious Metal Alloy Target
- High-purity targets suitable for various electrodes and metallization layers
- Film formation without defects such as pinholes, oxides, and gas
- Silver alloy targets with high environmental resistance (sulfuration and humidity resistance)

In the field of power devices, where further sophistication will be required in the future, we will maximize the potential of precious metal materials and, using our long-standing processing technologies, develop and provide various products that use elements other than precious metals. For details, please contact us.
Global Development System and Customer Service
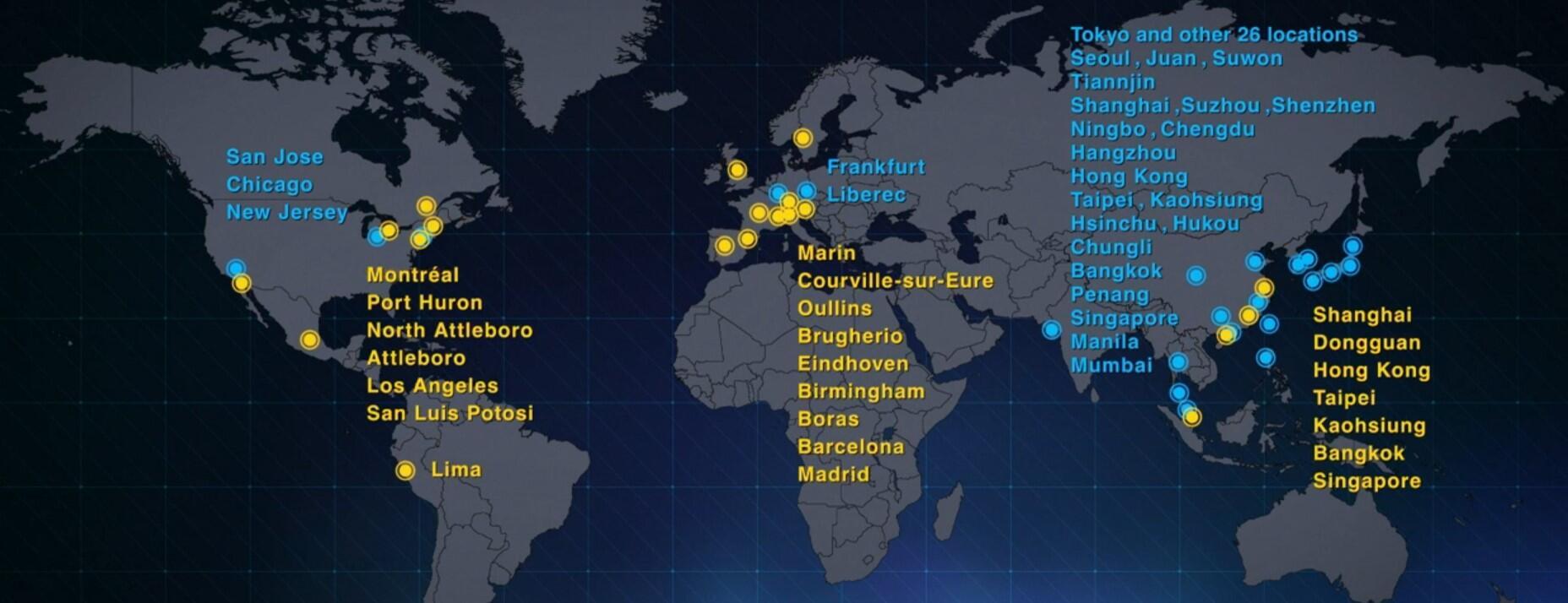
We leverage our strengths from many years of involvement in the semiconductor industry to provide total solutions.
- We have development sites around the world and can carry out speedy development and customer response according to our customers' needs.
- We have assembly and evaluation equipment similar to our customers' to accelerate the speed of development.
- From multiple product lineups, we can propose the optimal combination of materials that achieves both high reliability and high production efficiency.
- We have established a recycling scheme that converts materials containing precious metals, such as scraps generated during research and development and in the manufacturing process, back into pure precious metal bullion. We have also put in place a research and development system that allows us to repeatedly take on challenges using these valuable materials.